肺高壓定義 (2015 ESC Guildline for PH)
Mean pulmonary atery pressure > 25 mmHg
Echo findings suggest PH:
1. mild/moderate/severe TR, peak tricuspid regurgitation velocity: ____m/s, max PG:____ mmHg
(velocity <2.8/2.8-3.4/>3.4 m/s)
2. mild/moderate/severe PR, PG: ____ mmHg (<40/40-60/>60 mmHg)
3. PA acceleration time _____ ms Mean +/- 2 SD Accroding to Age/Sex/BW/HR
4. MPA diameter___ cm (對照Z score 肺高壓MPA會變粗)
5. Dilated RV.Flattening of the interventricular septum, RV base/LV base ratio ______
TV annulus/MV annulus about l, and >1 favor RV overload
Pressure or volume overload
6. IVC___cm with decreased inspiratory collapse (肺壓高吸氣IVC不容易collapse)
7. RA area ____ cm^2 (RA面積越大代表肺壓可能越高)
評估 Pulmonary artery systolic pressure (From Parasuraman S, Walker S, Loudon BL, et al. Assessment of pulmonary artery pressure by echocardiography-A comprehensive review. Int J Cardiol Heart Vasc. 2016;12:45-51. Published 2016 Jul 4. doi:10.1016/j.ijcha.2016.05.011)
1. Pulmonary artery systolic pressure by TR peak velocity
A value of ≤2.8 m/s suggests low probability, a value of 2.9–3.4 m/s indicates intermediate probability, and a value >3.4 m/s suggests a high probability for pulmonary hypertension
TR<2.8 m/s (31.36mmHg) : low probability for PH
TR= 2.9–3.4 m/s (32-46 mmHg) : intermediate probability for PH
TR>3.4 m/s (>46mmHg) : high probability for PH
Recent ESC guidelines suggest just using the TRmax without additional RAP,
as IVC assessment is error prone.
Mean PAP can be
approximated from the systolic PAP (SPAP) using the following formula:
mPAP = 0.61*SPAP + 2 mmHg
在ROVT stenosis or Pulmonary stenosis(PS)病人 Echo測到的PASP會高估,要減掉PS的壓力差
Mean PAP can be approximated from the peak PR Doppler signal using the following formula:
mPAP = 4(PRpeak velocity)2 + RAP
Mild/Moderate/Severe PR (<40/40-60/>60 mmHg)
mPAP = 2/3 PADP +1/3 PASP
PASP = 4TR^2 + RAP
PADP = 4(PR-end velocity)^2 + RAP
RAP=Right atrium pressure = CVC level = 2-6 mmHg (Normal condition)
4. Mean pulmonary artery pressure from right ventricular outflow tract (RVOT) acceleration time
RVOTAT = PAAT
> 130 ms = Normal
< 100 ms suggestive of pulmonary hypertension
*Heart rates outside of the normal range (<60 or >100 bpm) may reduce the accuracy of this technique. However, when the mean PAP exceeds 25 mmHg, RVOT acceleration time is accurate even in tachycardia
Right ventricular outflow tract (RVOT) acceleration time is measured from the beginning of the flow to the peak flow velocity.
Mean pulmonary pressure is calculated by the formula: mPAP = 90 − (0.62*ATRVOT).
For example, if the ATRVOT is 80 ms, the mPAP = 90−(0.62*80), that is 40.4 mmHg (normal b25 mmHg). On the other hand, if the ATRVOT is 137 ms (as in Fig. 4), then the calculated mPAP is 90−(0.62*137) = 5.06 mmHg.
5. Mean pulmonary artery pressure from TR velocity-time integral
CW Doppler of the TR jet is traced and the mean pressure difference is measured from the velocity-time integral (VTI)
RAP is then added to calculate the mPAP. Mean PAP measured by this method correlates closely with catheter-measured mPAP.
The mPAP from TR VTI can be calculated using the following formula: mPAP = meanΔP + RAP.
*A complete TR envelope may not be possible in all patients. Inaccurate RA pressure measurement leads to over or underestimation of mPAP.
6. RV free wall strain Sm, SmVTI
Tissue Doppler imaging (TDI) is used on the RV free wall in the apical 4-chamber view, and tricuspid annular systolic myocardial (Sm) velocity is recorded.
The maximal Sm velocity and the SmVTI are then measured (Fig. 6).
Sm velocity < 12 cm/s and SmVTI < 2.5 are highly suggestive of elevated PASP
• Obtain maximum TDI frame rate by narrowing the sector width.
• An RV-focussed apical 4-chamber view might reduce the incident angle on the tissue Doppler.
• A larger pulse gate might provide a complete signal, by capturing some of the myocardium throughout annular descent.
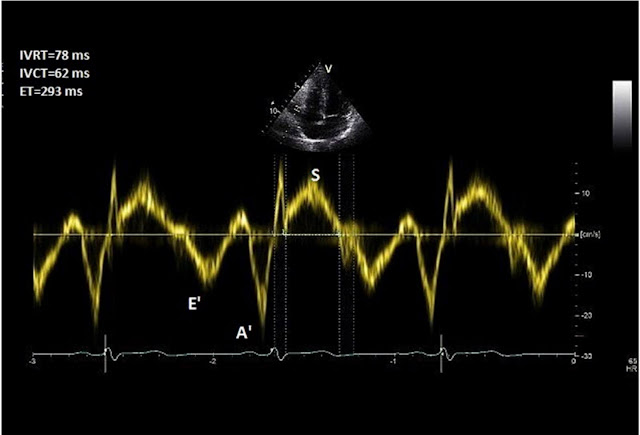
7. Right ventricular isovolumic relaxation time (rIVRT)
TDI is deployed at the lateral tricuspid annulus with a sweep speed of
100 mm/s.
Pulse wave (PW) Doppler with a 6 mm sample window is obtained.
Right ventricular isovolemic relaxation time (rIVRT) is measured
from
the offset of the S′ wave to the onset of the E’ wave (Fig. 7).
rIVRT >75 ms reliably predicts pulmonary hypertension while an rIVRT of <40 ms has a high negative predictive value for pulmonary hypertension
*Coaxial tricuspid TDI is may not be possible in all patients and incident angle should be no more than 15°. The technique may become unreliable in HCM , RBBB and RV dysfunction because therIVRT is prolonged for other reasons. rIVRT is pseudo-normalised in the presence of elevated RAP and significant TR
*When the HR is high, use the rate corrected rIVRT (r rIVRT’; which i.e. rIVRT/√RR interval on ECG)
2022/05/30 補充
用PA accerlation time 評估肺壓 以Philips CX50 sono為例
探頭轉到Long RVOT view 看清楚 pulmonary valve
將cursor對齊PA annulus 開口
開PW 如圖下所示 換算出來的壓力為 mean PAP
評估出的肺壓若為 51mmHg 則屬於 moderate pulmonary hypertension
分級如下表
Reference:
1. Assessment of pulmonary artery pressure by echocardiography-A comprehensive review. Int J rdiol Heart Vasc. 2016 Jul 4;12:45-51. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcha.2016.05.011. PMID: 28616542
2. 2015 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension















留言
張貼留言